2024 年单词量测试
去年测过,忘记记录结果了,好像是两千多还是三千多,今年打算每三个月测试一下,并记录结果,以检验学习成果。
测试网站 Test your
English vocabulary 20240102 测试结果: 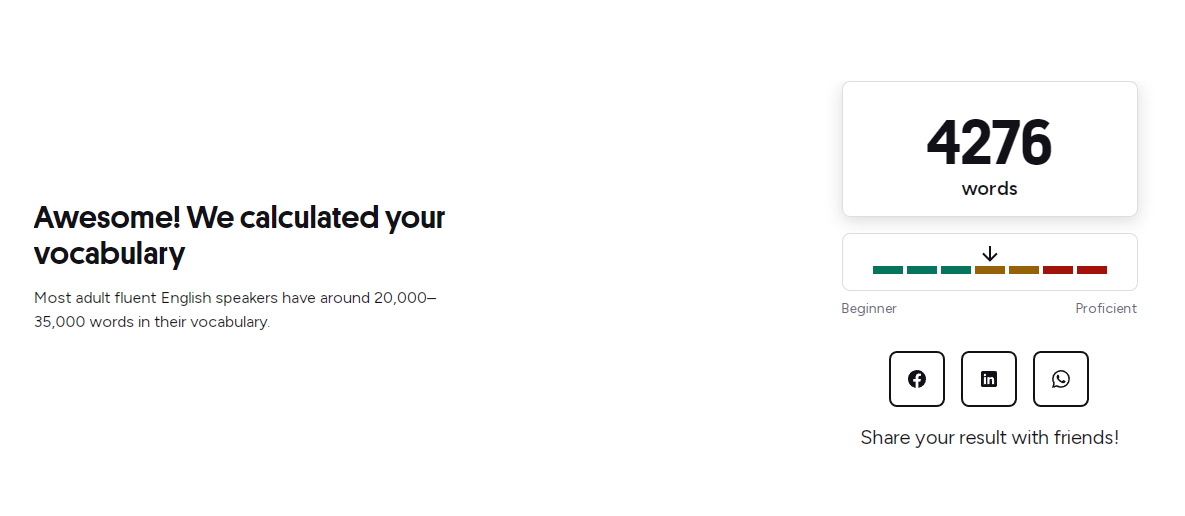
去年测过,忘记记录结果了,好像是两千多还是三千多,今年打算每三个月测试一下,并记录结果,以检验学习成果。
测试网站 Test your
English vocabulary 20240102 测试结果: 
2024 年希望自己保持积极乐观的心态,多学习,多运动,多阅读,多思考,多实践,多总结。 管理好自己的情绪,停止内耗,全力以赴追求自己想要的生活!
.livp 格式的文件修改后缀名为
.zip。可以使用一个批处理文件(.bat
文件)来完成这个操作。在任意一个文本编辑器中新建一个文件,输入以下命令:1 | ren *.livp *.zip |
然后将这个文件保存为 .bat 格式,例如
rename_to_zip.bat。将这个文件放到需要修改后缀名的文件夹中,双击运行即可。
使用 WinRAR 软件批量解压缩 .zip
格式的文件。下载并安装 WinRAR
软件,然后选中需要解压缩的文件夹,右键点击选择“解压到指定文件夹”,选择目标文件夹,点击“确定”即可完成批量解压缩。
使用 HEIC Utility 软件批量将 .heic 格式的文件转换为
.jpeg 格式。下载并安装 HEIC Utility
软件,打开软件,在菜单栏选择 更多 -> 批量转换,点击右上角的
+ 号,选择上一步解压的文件夹里的所有 .heic
格式的文件,在左下角设置输出目录和输出质量,最后点击“开始转换”按钮即可完成批量转换。
本文转载自 如何禁止别人调试自己的前端代码,此处仅作记录。
前端页面防止调试的方法主要是通过不断 debugger 来疯狂输出断点,因为 debugger 在控制台被打开的时候就会执行。由于程序被 debugger 阻止,所以无法进行断点调试,所以网页的请求也是看不到的。 以下是使用无限 debugger 方式阻止代码调试的示例:
1 | /** |
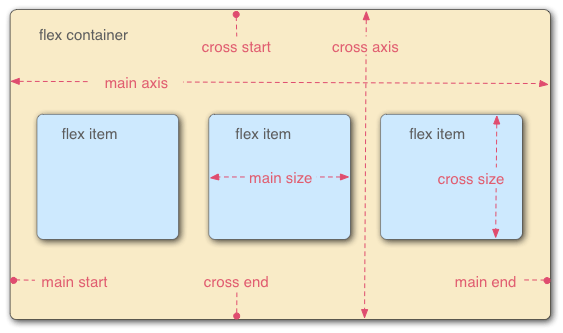
FLEXBOX CSS3 中的一种布局模式,它可以帮助开发者更加方便地实现自适应布局和响应式设计。FLEXBOX 基于弹性盒子模型,通过对容器和容器内元素的属性设置来实现灵活的布局。
在 FLEXBOX 中,容器是指设置了 display:flex 或 display:inline-flex 属性的元素,容器内的元素则是指容器的子元素。通过设置容器和容器内元素的属性,可以实现以下功能:
弹性布局:容器内的元素可以根据容器的大小和方向自动调整位置和大小,从而实现弹性布局。
对齐方式:可以通过设置 justify-content 和 align-items 属性来实现容器内元素的水平和垂直对齐。
排列方式:可以通过设置 flex-direction 属性来实现容器内元素的排列方式,包括水平排列和垂直排列。
元素间距:可以通过设置 justify-content 和 align-items 属性来实现容器内元素的间距和间隔。
元素排序:可以通过设置 order 属性来实现容器内元素的排序,从而实现元素的前后顺序调整。